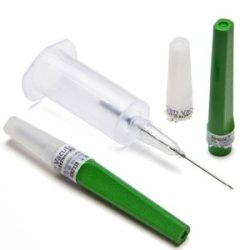
Disposable Blood Collection Tubes Plastic/Glass EDTA K2/K3
Agna Healthcare has been committed to the R&D, production, and sales of a series of products for medication administration, enteral Feeding Set, blood sample collection, modern wound care, and surgical drainage, etc.
- Home
- Product
- Disposable Blood Collection Tubes Plastic/Glass EDTA K2/K3
Descriptions
BLOOD COLLECTION TUBE
The whole blood collection tube provides a contaminant-free and undifferentiated blood sample for medical tests that do not require the separation of plasmas or cells.
This segment includes 2 types of tubes: EDTA 7.2mg tube (purple cap) and ESR tube (black cap).
The EDTA tube is widely used for hematology testing, especially for hematological cell analysis. Our automatic sampling instrument sprays EDTA additive finely and precisely onto the inner wall of the tube to ensure mixing and anticoagulant effect. The EDTA tube is very convenient for use in automatic analyzers as it can be placed directly into the analyzer without opening the cap.
Storage: Store the tubes at 4-25 ºC, unless otherwise specified on the package label.
Expiration Time: 18 months
Recommended Drawing Order:
1. Sterile sample tubes.
2. Tubes for coagulation studies (e.g. citrate).
3. Tubes for serum collection.
4. Tubes with other additives (e.g. heparin, EDTA, fluoride).

Caution:
1. Follow universal precautionary practices. Use gloves, gowns, eye protection, and other personal protective equipment, as well as engineering controls to protect against blood splashes and leaks and potential exposure to blood-borne pathogens.
2. Handle all biological specimens and blood collection sharps (lancets, needles, connection adapters, and blood collection sets) according to your facility’s policies and procedures. Obtain appropriate medical care if you are exposed to any biological specimens (such as a needle stick injury), as they may transmit viral hepatitis, HIV infection (AIDS), or other infectious diseases. Use any built-in needle guards.
3. Dispose of all blood collection sharps in approved biohazard containers for disposal.
4. Transferring a specimen collected by syringe and needle to a tube is not recommended. Additional handling of sharps, such as needles with a cavity inside, increases the chance of accidental needle sticks.
5. Transfer of specimens from a syringe to a vacuum collection tube using a non-sharp device should be done with caution for the following reasons. • Depressing the syringe plunger during transfer can create positive pressure that forcibly displaces the stopper and specimen, causing
splattering and exposure to blood. • Using a syringe to transfer blood can also cause overfilling or underbilling of the tubes, resulting in
incorrect blood-to-additive ratios and the possibility of incorrect analytical results. • Vacuum collection tubes are designed to
withdraw the indicated volume. The filling is complete when the vacuum stops drawing, although some tubes may be partially filled due to plunger resistance
when filled with a syringe. The laboratory should be consulted regarding the use of these specimens.
6. If blood is collected through an intravenous (IV) line, make sure the line is clear of IV solution before you begin filling the blood collection tubes. This is critical to avoid erroneous laboratory data due to contamination with IV fluid.
7. Uncontrolled endotoxin. The blood and blood components collected and processed in the tube are not intended for infusion or introduction into the human body.
8. Do not write on or cover the barcode areas, as sample identification may be affected.
Search
Emergency?
24 Hour Ready
Call Us for Emergency
86 - 18366213173
Product Categories
- Anesthetic Products
- Automatic Extracorporeal Defibrillator
- Bandage
- Blood Sample Collection
- Coveralls
- Disposable Gloves
- Disposable Masks
- Disposable Syringe
- Dranaige Catheter
- First Aid Kits
- Infusion Products
- Isolation Gowns
- IV Catheter
- Lab Coats
- Medical Administration
- Medical Comprehensive
- Medical Instruments
- Modern Wound Care Products
- Patient Gowns
- PPE Products
- Protowels/Paper Roll
- Respiratory Care
- Scrub Suit
- Sharp Containers
- Stretchers & Emergency Beds
- Surgical Gowns
- Surgical Packs
- Surgical Suture & Needles
- Uncategorized
- Underpads/Diapers
- Urostomy Bags
- Urulogy
- Wound Care Products
Products
Related Products
Related products
-
Blood Sample Collection
Disposable blood lancet all sizes
-
Blood Sample Collection
Vacutainer Blood Sample Tube Plastic Light Blue 2.7ml 1×100
-
Blood Sample Collection
Blood Collection Needle All sizes 21G-30G
-
Blood Sample Collection
Disposable capillary blood collection tube






-250x250.png)